Toyota’s Enduring Four-Cylinder Workhorse
The Toyota 3RZ-FE earned a reputation for durability rarely matched among four-pot engines. Produced between 1994 and 2004, this 2.7-litre inline-four replaced the long-serving 22R-E and found its way into run-tough models like the Tacoma and 4Runner, while also powering global models such as the Toyota Hilux, Land Cruiser Prado, and the Hiace van.
The 3RZ’s design blended rugged traditional components – such as a deep-skirt cast-iron block, forged crankshaft with eight counterweights, and carbon-steel, shot-peened rods – with practical enhancements like oil jets under the pistons for improved cooling. These features helped the 3RZ-FE remain dependable in heavy-use contexts.
Yet, as this teardown of an engine with over 300,000 miles revealed, even such a solid structure can fail if the owner overlooks basic maintenance.
The Engine Teardown Revealed the Most Evident Culprit
In the video, the engine rotates freely and shows signs of uneven spark plug readings, pointing to lean or rich combustion in different cylinders. Removing the valve cover exposes coolant-contaminated oil – a clear sign of a blown head gasket, as confirmed by the distorted appearance of a cylinder, which was caused by coolant wash.
Despite this failure, internal components appear remarkably intact. The camshafts and journals show minimal wear, and the crankshaft is in excellent condition. The bearings, likely original, look surprisingly healthy given the mileage.
Meanwhile, the pistons surprisingly show normal wear with minor damage from the head gasket breach. The timing chain and guides – still serviceable after decades – highlight how Toyota over-engineered this non-2JZ power plant.
I Do Cars/YouTube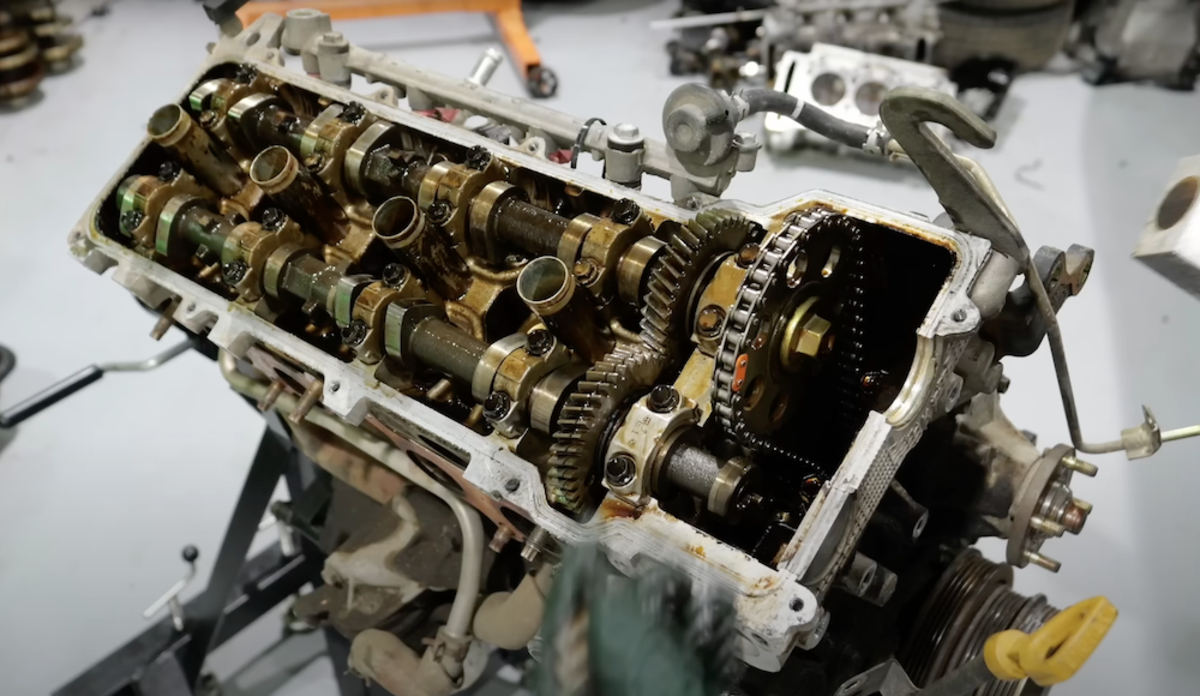
What Keeps the 3RZ-FE Running for Decades
This teardown reaffirms why the 3RZ-FE remains sought after, particularly in used markets or rebuild projects. Its straightforward design – inline-four, timing chain, and robust materials – makes it low-tech by modern standards but reliable in real-world use.
Still, that reputation is conditional. Common weak spots include valve clearance adjustments (required every 25,000-30,000 miles), timing chain wear (check around 100,000-120,000 miles), balance shaft bearing issues, and water pump failures – each can lead to critical failures if ignored.
Owners should watch for heat-related warning signs: oil that looks contaminated, white smoke from the exhaust, or rising engine-temperature readings. Timely coolant system maintenance – like swapping the water pump, radiator, hoses, and thermostat – can prevent overheating that leads to head gasket failure.
Toyota






